History (Before Virtualization)...🙄
In the past, when Virtualization was not born yet, the industry people used to run different services on different servers. For example, if anyone needs to run a Web service or any other service, he/she has to buy physical hardware (server), also called "Bare Metal Server". The fun fact or pain fact 😶 is that one server can only run a single task that is allocated to it. This means, to run the web service you'll buy a server but, to hold the data of the website at the backend -> you'll again buy another server 🙂. So, just to run a single service, people used to buy multiple Bare Metal Servers, and *note that => Single server will have one OS installed on it, which will run only one service.
Now, let's visualize this scenario with a real-life case study of a company...
If a company doesn't use Virtualization technology, firstly it will buy huge land, to build the data center.
Now, inside the data center, there will be multiple Bare Metal servers for the operation of global business.
Now, to run the global business consistently, the servers must run day and night, which will generate a lot of heat, so to overcome that, the company requires AC running 24 hr.
Now, to run all the appliances there must be Electricity and Power Backup so that servers don't go down.
Finally, to manage the data center, the company will hire staff.
Now, if we calculate the Capex and Opex of the company, it will be a lot, and there might be the case that the company's server is working only for 2 days in a month (Ex: Employee's salary server), but still, the company has to invest.
So, what is the solution? => "Virtualization".
What junk is Virtualization?
Virtualization is the technique of splitting the physical resource (server) into multiple logical resources. This means that we can run multiple Virtual Machines of different OS (like MacOS or any Linux distros) on a single physical server.
It is a technology that transforms hardware into software.
To virtualize your physical resources (RAM, storage, cores, etc.), a software called "Hypervisor" is installed on the physical server. This Hypervisor is the one, which takes the resources (RAM, storage, cores, etc.) from the physical server and split those resources into logical or virtual resources.
Now, there are 2 types of Hypervisors:- "Type 1 Hypervisor" (also called Bare Metal or Native) and "Type 2 Hypervisor" (also called Hosted).
Type-1 Hypervisor is the one that is directly installed on the Physical server and is mostly used in industries. As this hypervisor runs directly on the hardware, therefore it is called "Hardware Virtualization", whereas, Type-2 Hypervisor is the one that is installed on the Host OS and is mostly used for practice purposes by students. As this hypervisor runs on the OS, therefore it is called "OS Virtualization".
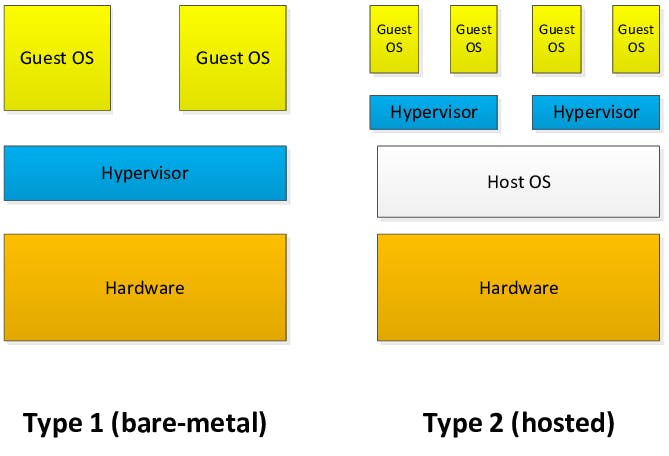
Examples of Type-1 Hypervisor are => VMware's ESXI, Microsoft's HyperV, Amazon's Xenserver or Nitro, etc. As VMware was the first company to run multiple OS on a single physical machine, therefore VmWare's hypervisor (ESXI) is majorly preferred
Examples of Type-2 Hypervisor are => VMware's Workstation and Oracle Virtual Box.
Quick Fact About Virtualization
Most people think that Virtualization only means "splitting of physical resources into virtual resources" but, it also means "adding the physical resources and creating one logical resource".
Let's understand this concept with an example:
Let's assume that "NASA" wants to store there 150TB of data collectively into a Physical server, but the problem is that, the maximum storage of the physical server that we get is 50TB. Now, how can NASA store its data collectively => The answer is "Virtualization".
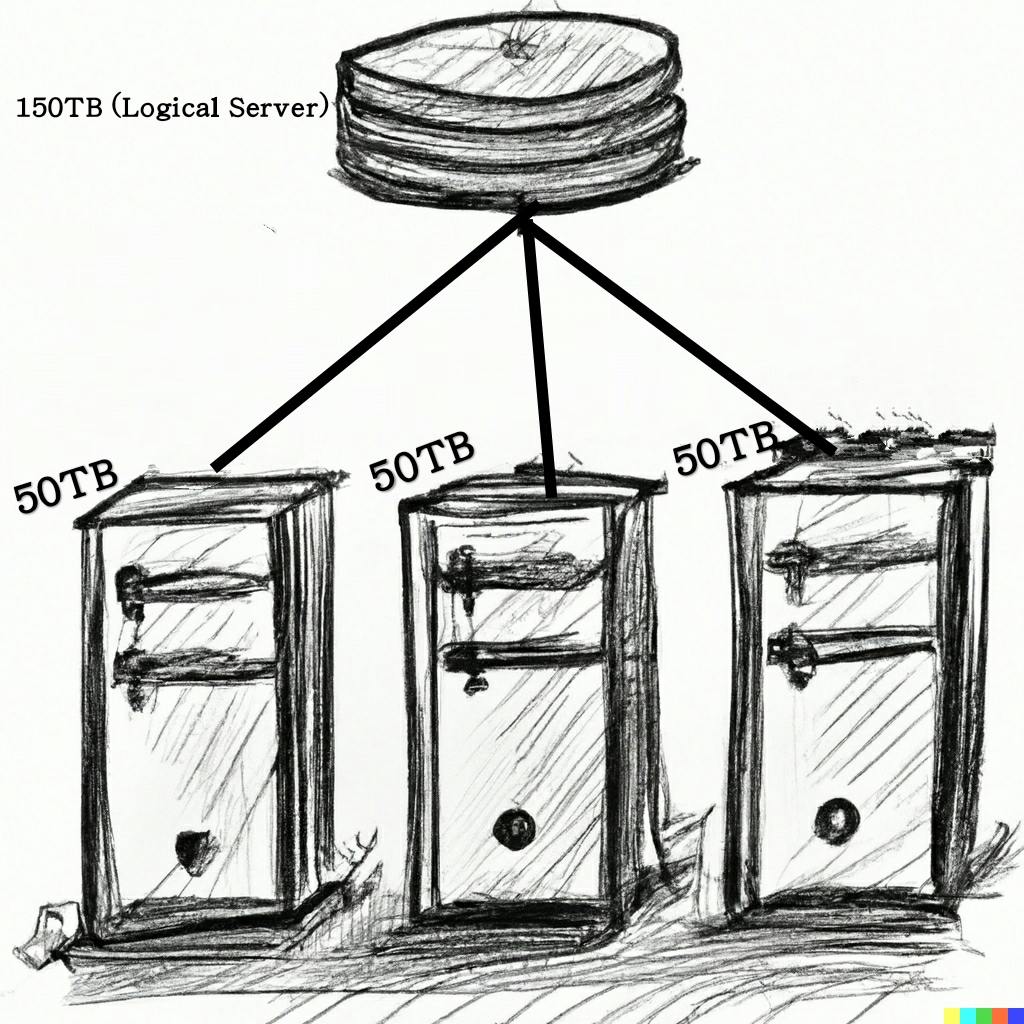
They can combine 3 Physical servers of 50TB and can use them as a single Logical server.
*Note that The data is being stored in these physical servers only but, these 3 physical servers are just acting as a single unit.
Now the question rises, How data is kept inside this single-unit logical server's storage? => Here comes the concept of "Logical Unit Number". The storage that is combined inside the logical server is divided into the block structure, where the data is stored.
The problem with this is, if one of the physical servers fails, the whole data kept inside will get corrupted because all 3 physical servers are connected.
Uses of Virtualization
There is no need to buy huge land for creating a data center and keeping multiple physical servers, as with Virtualization, the company can run multiple virtual servers on a single hardware server.
Now, here the question rises, if the virtual servers are running on one physical server, then, there can be security breaches as well. => The answer is "NO". Just like there are physical servers that run different services and neither of the physical server care about each other, Similarly, Virtual servers running beside each other doesn't care. Each virtual server acts as if there is no other server present.
As, the company doesn't need to buy many physical servers, therefore the cost of the cooling system, electricity, and maintenance of servers will be reduced.
Overall, the Capex and Opex of the company will be reduced by 85-90%, therefore, with Virtualization technology, the company can save a lot of its initial investment.
Bonus Point:
In the Physical environment -> The servers are 1:1 (i.e. One server will run One service only)
But, In a Virtual environment -> The servers are 1:n (i.e. One server can run n number of Virtual Servers and on those virtual servers, we can run the dedicated service). But always remember, even if it is a Virtual server, it will run ONE service only.
In 1:n, "n" does not mean unlimited or infinite. It depends on the physical server's configuration. (Ex: If the RAM of the physical server is 16GB, and we allotted 4GB of each RAM to the virtual server, then only 4 virtual servers will be created). So, n is directly proportional to the resources of the physical server.
Extra Resources...
Apart from reading this blog, if you want to know more about this technology, then you can refer to these resources:-
Resource-3 (VMware_Virtualization_tutorial)